Targeted molecular profiling uncovers true ceruminous adenomas with HMGA2::WIF1 and ceruminous syringocystadenoma papilliferum with BRAF V600E.
Virchows Arch. 2025 Nov 20. doi: 10.1007/s00428-025-04256-6. Online ahead of print.
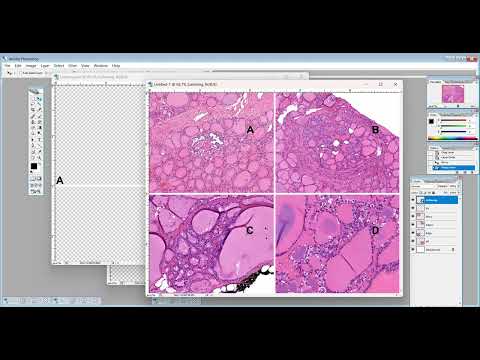
Ceruminous adenomas are benign neoplasms that arise from ceruminous glands in the external auditory canal. While these tumors are currently regarded as a single entity, they are divided into three histologically diverse subtypes: ceruminous syringocystadenoma papilliferum, ceruminous pleomorphic adenoma, and ceruminous adenoma not otherwise specified (NOS). Given the similarities of two of these subtypes to other tumors that occur at multiple anatomic sites, it is currently unclear whether ceruminous adenomas are truly a unified group. In this study, we performed targeted molecular profiling of 11 cases of ceruminous adenoma to clarify their classification. We identified BRAF V600E mutations (via PCR and/or immunohistochemistry) in five ceruminous syringocystadenomas papilliferum. We also identified HMGA2::WIF1 fusions (via RNA sequencing) in five ceruminous adenomas NOS and one ceruminous pleomorphic adenoma. Tumors with HMGA2::WIF1 fusion did not display the canalicular adenoma-like morphology seen in salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas with this fusion. Overall, these findings suggest that the three subtypes of ceruminous adenoma represent two biologically distinct groups. Recurrent BRAF V600E mutations in ceruminous syringocystadenoma papilliferum are parallel to those in cutaneous syringocystadenoma papilliferum. Histologic and molecular concordance suggests that ceruminous syringocystadenoma papilliferum should be part of the broader syringocystadenoma papilliferum category rather than a subtype of ceruminous adenoma. Conversely, HMGA2::WIF1 fusions in ceruminous adenoma NOS and ceruminous pleomorphic adenoma suggest that a stromal component may not be an essential point of distinction between these groups. These residual true ceruminous adenomas all likely represent a specialized form of mixed tumor unique to the external ear.
PubMed ID: 41266927
Article Size: 3.44 MB


 Current 5th Edition
Current 5th Edition 4th Edition
4th Edition 3rd Edition
3rd Edition
 Current 5th Edition
Current 5th Edition
 Subscribe
Subscribe